CONDITIONS
SYMPTOM CHECKER
Male
Female
Child
Arm, Hand & Shoulder Concerns
Legs & Feet Concerns
Dental & Mouth Concerns
Ear & Nose
Eye Conditions
Head Conditions
Arm, Hand & Shoulder Concerns
Legs & Feet Concerns
Front
Back
Arm, Hand & Shoulder Concerns
Dental & Mouth Concerns
Ear & Nose
Eye Conditions
Head Conditions
Arm, Hand & Shoulder Concerns
Dental & Mouth Concerns
Ear & Nose
Eye Conditions
Head Conditions
Front
Back
Arm, Hand & Shoulder Concerns
Neck Links
Head & Neck Concerns
Arm, Hand & Shoulder Concerns
Neck Links
Head & Neck Concerns
Front
Back
Online Clinic
Wise Healthcare
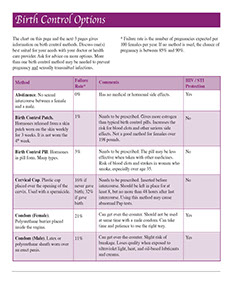
Birth Control Options
Abstinence | Birth Control Patch | Birth Control Pill | Cervical Cap | Condom (Female) | Condom (Male) | Depo-Provera | Diaphragm | Emergency Contraception Pills | Emergency IUD Insertion | FemCap® | Implanon® | Intrauterine Device (IUD) | Intrauterine System (IUS) | Lea's Shield® | Natural Family Planning | NuvaRing® | Spermicides | Today Sponge® | Sterilization (Female) | Sterilization (Male) | Withdrawal
Print on Demand
RELATED ARTICLES
This page gives information on birth control methods. Discuss one(s) best suited for your needs with your doctor or health care provider. Ask for advice on more options. More than one birth control method may be needed to prevent pregnancy and sexually transmitted infections.
* Failure rate is the number of pregnancies expected per 100 females per year. If no method is used, the chance of pregnancy is between 85% and 90%.
Abstinence
No sexual intercourse between a female and a male.
Has no medical or hormonal side effects.
Failure Rate*
0%
HIV / STI Protection
Birth Control Patch
Hormones released from a skin patch worn on the skin weekly for 3 weeks. It is not worn the 4th week.
Needs to be prescribed. Gives more estrogen than typical birth control pills. Increases the risk for blood clots and other serious side effects. Not a good method for females over 198 pounds.
Failure Rate*
1%
HIV / STI Protection
Birth Control Pill
Hormones in pill form. Many types.
Needs to be prescribed. The pill may be less effective when taken with other medicines. Risk of blood clots and strokes in women who smoke, especially over age 35.
Failure Rate*
3%
HIV / STI Protection
Cervical Cap
Plastic cap placed over the opening of the cervix. Used with a spermicide.
Needs to be prescribed. Inserted before intercourse. Should be left in place for at least 8, but no more than 48 hours after last intercourse. Using this method may cause abnormal Pap tests.
Failure Rate*
16% if never gave birth; 32% if gave birth
HIV / STI Protection
Condom (Female)
Polyurethane barrier placed inside the vagina.
Can get over-the-counter. Should not be used at same time with a male condom. Can take time and patience to use the right way.
Failure Rate*
21%
HIV / STI Protection
Condom (Male)
Latex or polyurethane sheath worn over an erect penis.
Can get over-the-counter. Slight risk of breakage. Loses quality when exposed to ultraviolet light, heat, and oil-based lubricants and creams.
Failure Rate*
11%
HIV / STI Protection
Depo-Provera
Hormone given through a shot every 3 months.
Needs to be prescribed. May cause irregular periods, weight gain, fatigue, and headaches. Once stopped, it can take 4 to 18 months for a woman to be fertile again. Can cause bone loss if taken for more than 2 years.
Failure Rate*
Less than 1%
HIV / STI Protection
Diaphragm
Reusable, thin, soft, rubber cap that covers the cervix. Used with a spermicide.
Needs to be prescribed. Should be checked for leaks. Size may need to be changed with weight changes. May dislodge during intercourse. Should be left in place at least 6, but no more than 24 hours, after last intercourse.
Failure Rate*
6% to 16%
HIV / STI Protection
Emergency Contraception Pills
High-dose birth control pills that need to be started within 72 hours after unprotected intercourse. Called “morning after pill.”
Can get over-the-counter if age 18 years and older. Needs to be prescribed for females age 17 and younger. The pills are taken in 2 doses, 12 hours apart. Can cause nausea, vomiting, breast tenderness, infertility, and blood clots.
Failure Rate*
11% to 25% (the sooner used, the more effective)
HIV / STI Protection
Emergency IUD Insertion
Needs to be done within 7 days of unprotected intercourse.
Needs to be done by a health care professional.
Failure Rate*
Less than 1%
HIV / STI Protection
FemCap®
Silicone rubber device. Fits snugly over the cervix.
Needs to be prescribed. Should be left in place for at least 6, but no more than 48 hours, after last intercourse.
Failure Rate*
14% if never gave birth; 29% if gave birth
HIV / STI Protection
Implanon®
Thin plastic implant about the size of a match stick. Releases a low dose of the hormone progestin for up to 3 years.
Needs to be inserted and removed by a health care professional. Can cause irregular menstrual bleeding, mostly fewer and lighter periods, or no periods.
Failure Rate*
Less than 1%
HIV / STI Protection
Intrauterine Device (IUD)
ParaGard. Small copper device inserted into uterus.
{Note: An IUD does not prevent an ectopic pregnancy. With this, an embryo starts to grow outside the uterus. Most often, this is in a fallopian tube.}
Needs to be inserted and removed by health care professional. Can be left in place for up to 12 years. May become dislodged. Risk of infection and piercing of the uterus. Need to learn how to check for the 2 strings that hang from the bottom of the IUD to make sure it is in the right position.
Failure Rate*
Less than 1%
HIV / STI Protection
Intrauterine System (IUS)
Mirena®. T-shaped device placed in uterus. Releases low dose of hormones every day for 5 years.
Needs to be inserted and removed by a health care professional. May lessen menstrual cramps. Needs to be replaced every 5 years.
Failure Rate*
Less than 1%
HIV / STI Protection
Lea's Shield®
Silicone cup with an air valve and a loop (aids in removal) that fits snugly over the cervix. Used with a spermicide.
Needs to be prescribed. Should be left in place at least 8, but no more than 48 hours, after last intercourse.
Failure Rate*
15%
HIV / STI Protection
Natural Family Planning
Ovulation signs need to be checked for and kept track of.
Sexual intercourse must be limited to “safe” days. Takes training, time, and record keeping to work right. Method for planning a pregnancy, too.
Failure Rate*
20%
HIV / STI Protection
NuvaRing®
A soft, flexible ring that a female inserts deep into the vagina. Contains hormones.
Needs to be prescribed. A new Ring is inserted once and kept in place for 3 weeks. It is removed the week of menstrual period. May cause increased risk for vaginal problems.
Failure Rate*
1% to 5%
HIV / STI Protection
Spermicides (Foams, Jellies, Creams)
Chemicals inserted into the vagina kill sperm before it enters the uterus.
Can get over-the-counter. More reliable when used with condoms, diaphragms, etc. Inserted between 5 and 90 minutes before intercourse. Need to reapply for repeated acts of intercourse.
Failure Rate*
15 to 21%
HIV / STI Protection
Today's Sponge®
Polyurethane barrier that contains spermicide.
Can get over-the-counter. Must be left in place for 6 hours after last intercourse, but should not be worn for more than 24 hours after sex.
Failure Rate*
9% to 19%
HIV / STI Protection
Sterilization (Female)
Tubal ligation (having the tubes tied). This surgery burns, cuts, blocks, or ties off the fallopian tubes. Another type, tubal implants (Essure®), is not surgery. A device is inserted through the vagina and uterus into each fallopian tube. This causes scar tissue to grow and plug the tubes.
Permanent form of birth control. Should be used only when no more children are desired. Surgery usually needs general anesthesia. Sterilization implants do not.
Failure Rate*
Less than 1%
HIV / STI Protection
Sterilization (Male)
Vasectomy. The tubes through which sperm travels from the testes are cut.
Permanent form of birth control. Done in an outpatient setting with local anesthesia. Not effective right away. Sperm can still be present for 20 ejaculations.
Failure Rate*
Less than 1%
HIV / STI Protection
Withdrawal
The penis is removed before ejaculation.
Have to control ejaculation. Sperm can leak before this occurs.
Failure Rate*
Up to 27%
HIV / STI Protection
No
This website is not meant to substitute for expert medical advice or treatment. Follow your doctor’s or health care provider’s advice if it differs from what is given in this guide.
The American Institute for Preventive Medicine (AIPM) is not responsible for the availability or content of external sites, nor does AIPM endorse them. Also, it is the responsibility of the user to examine the copyright and licensing restrictions of external pages and to secure all necessary permission.
The content on this website is proprietary. You may not modify, copy, reproduce, republish, upload, post, transmit, or distribute, in any manner, the material on the website without the written permission of AIPM.
2021 © American Institute for Preventive Medicine - All Rights Reserved. Disclaimer | www.HealthyLife.com