First Aid
Stroke (Brain Attack)
A stroke is also called a “brain attack.” With a stroke, brain cells die due to a blood clot or rupture of a blood vessel in the brain. The end result is brain damage (and possible death).
In the U.S., strokes are the 3rd leading cause of death. They are the leading cause of adult disability.
Signs & Symptoms
• Sudden numbness or weakness of the face, arm, or leg, especially on one side of the body.
• Sudden confusion, trouble speaking or understanding.
• Sudden trouble seeing in one or both eyes.
• Sudden trouble walking, dizziness, loss of balance or coordination.
• Sudden severe headache with no known cause.
Causes
Most strokes are caused by a blood clot in an artery in the neck or brain. Some are caused by bleeding into or around the brain.
Risk Factors for a Stroke
• Previous stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA)—a temporary lack of blood supply to the brain.
• Atrial fibrillation. This is an irregular beating of the heart.
• High blood pressure. Cigarette smoking. Diabetes. Coronary artery disease.
• Being a male over age 70.
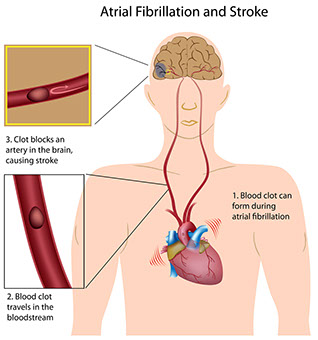
Prevention
• Take medicine(s), as prescribed, to control blood pressure, blood cholesterol, diabetes, and atrial fibrillation. Aspirin may help reduce the risk of stroke in women ages 55-79 years. Discuss this with your doctor.
• Get to and stay at a healthy weight. Get regular exercise.
• Don’t smoke. If you smoke, quit. Use alcohol in moderation. Manage stress.
Questions to Ask
Question
01
Does any stroke warning sign occur? {Note: Call 9-1-1 without delay! Then, follow first aid listed on this page.}

Get medical care without delay. If symptoms are life threatening go to the ER or call 9-1-1. Don’t call 9-1-1 or use the ER if symptoms do not threaten life. Ask your doctor ahead of time where you should go for a problem that needs prompt care, but not emergency care.
x
Question
02
In the past, have stroke warning signs occurred briefly and then gone away?
You should be seen by your doctor for medical advice. Contact your doctor or health care provider to find out how soon you should be seen.
x
Self-Care / Prevention
First Aid before Emergency Care
• Note the time when the first sign(s) of stroke occurred. Report this time to emergency personnel. For the most common type of strokes, a clot-busting drug should to be given within 3 hours of the start of symptoms.
• Do not give the person anything to eat or drink. Do not give aspirin.

Download an offline pdf file.
RELATED ARTICLES
<
>
2021 © American Institute for Preventive Medicine - All Rights Reserved. Disclaimer | www.HealthyLife.com








