Skin cancer is the most common kind of cancer in the U.S.
When found early, skin cancer can be treated with success.
Skin Cancer Warning Signs
Contact your doctor if you notice any of these following signs below.
For basal cell and squamous cell skin cancers (types that seldom spread to other parts of the body):

Video


Questions to Ask

Self-Care / Prevention
Prevention should start in childhood to prevent skin cancer later in life.
-
•Avoid exposure to midday sun (10:00 a.m. to 4:00 p.m. standard time; 11:00 a.m. to 5:00 p.m. daylight saving time).
-
•Use a sunscreen with a sun protection factor (SPF) of 15 or higher as directed.
-
•Avoid sun lamps and tanning salons.
Skin Self-Exam
-
•Do a skin self-exam monthly. The best time to do this is after a shower or bath. To check your skin, use a well-lit room, a full-length mirror, and a hand-held mirror.
-
•Locate your birthmarks, moles, and blemishes. Know what they look like. Check for a sore that does not heal.
-
•Check all areas.
-
•Look at the front and back of your body in the mirror. Then, raise your arms and look at the left and right sides.
-
•Bend your elbows and look carefully at the palms of your hands. Make sure to look at both sides of your forearms and upper arms.
-
•Look at the back and front of the legs. Look between the buttocks and around the genital area.
-
•Look at your face, neck, and scalp. Use a comb or blow dryer to move hair so that you can see the scalp better.
-
•Sit and closely examine the feet. Look at the soles and the spaces between the toes.
{Note: Get a skin exam from your doctor or health care provider as often as advised.}
Common Health Problems » Skin Conditions

Do you have any skin cancer warning sign listed above?

Most dermatologists recommend examining your skin once a month to become familiar with what it looks like normally—so you'll be able to recognize something that's abnormal. And since skin cancer is curable if caught in an early stage, your life just might depend on it.

Causes
-
•Recurrent exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun is the main cause.
-
•Artificial sources of UV radiation, such as sun lamps and tanning beds.
Risk Factors
-
•Having skin cancer in the past.
-
•A family history of skin cancer.
-
•Having fair skin that freckles easily, especially with red or blond hair and blue or light-colored eyes.
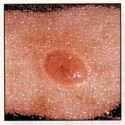
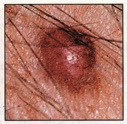

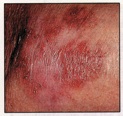
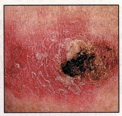
Small, smooth, shiny, pale, or waxy lump
Firm red lump
A lump that bleeds or develops a crust
A flat, red spot that is rough, dry, or scaly
For melanoma (can spread to other parts of the body and be fatal if not treated early). Look for any of these signs in an existing mole:
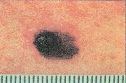
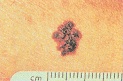
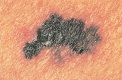
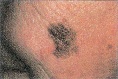
A. Asymmetry - The shape of one half does not match the other.
B. Border - The edges are ragged, notched or blurred.
C. Color - The color is uneven.
D. Diameter - The size changes and is often bigger than a pencil eraser.
E. Evolving lesion - This is one that changes size, shape, shades of color or symptoms or has surface bleeding.


Resources



HealthyLearn®
www.HealthyLearn.com. Click on MedlinePlus®.

Treatment


Depending on the size, type, and stage of the cancer, treatment includes:
-
•Surgery. There are many types.
-
•Laser therapy.
-
•Chemotherapy. One form is a cream or lotion with anticancer drugs that is applied to the skin. Other forms are given through an IV.
-
•Radiation therapy.
-
•Interferon drugs.
-
•Skin grafting.



2012 © All Rights Reserved - American Institute for Preventive Medicine | Disclaimer | Phone: 800.345.2476 | www.HealthyLife.com