-
Skin Conditions




Warts
Warts are small skin growths. Most are harmless and painless. They can appear on any part of the body.
Signs & Symptoms
-
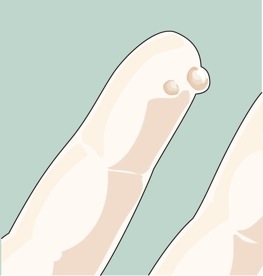
•Common warts. These are firm and often have a rough surface. They are round or have an irregular shape. They are found on places subject to injury, such as the hands, fingers, and knees. Common warts are flesh-colored to brown. They may spread, but are not cancer.
-
•Flat warts. These are smooth and flesh-colored. They are found mainly on the hands and face and may itch.
-
•Plantar warts. These occur on the soles of the feet. They look like corns or calluses and may have little black dots in the center. They can be painful.




Common warts.
-
•Digitate warts. These threadlike warts grow on the scalp.
-
•Filiform warts. These are long, narrow, small growths. They appear mainly on the neck, eyelids, or armpits.
-
•Genital warts. (See STI’s – Human Papillomavirus (HPV).)
Causes
Warts are caused by human papillomaviruses. One of these viruses may enter the body through a cut or nick in the skin. Scratching or picking at warts may spread them to other sites. Some persons are more prone to getting warts than others. People who cannot fight off disease are also more at risk for warts. You cannot get warts from frogs or toads.
Treatment
Treatment for warts depends on their location, type, and severity and how long they have been on the skin. About 50% of warts go away in 6 to 12 months without treatment.
Self-care measures can be used for warts not on the face or genitals. Medical treatment includes liquid nitrogen, chemical injections, topical medicines, laser surgery, and minor surgery. For genital warts, see Treatment in STIs – Human Papillomavirus (HPV).
Are any of these problems present?
-
•The wart is near the genital or anal area.
-
•The wart is painful.
-
•The wart has changed its shape or color.
-
•Signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, pain, drainage, warmth, or red streaks occur at the wart site.
-
•The location of the wart limits normal movement.
-
•The wart is a new wart on a person over 45 years old.
Do any of these problems occur?
-
•The wart is bothersome and has not responded to self-care measures.
-
•The wart has been irritated or ripped off.
-
•The wart is on the face and you want it removed.
-
•Multiple warts are present.
Self-Care / Prevention
-
•Don’t touch, scratch, or pick at warts.
-
•Never cut or burn a wart off.
-
•Try an over-the-counter wart remover with salicylic acid. This can be a liquid or it can be in a medicated wart pad or patch. {Note: Do not use these wart removers on the face or genitals.} Follow package directions. A pumice stone helps remove the dead skin during this treatment.
-
•Ask your doctor about Retin A for flat warts.
-
•During treatment for plantar warts, put pads or cushions in your shoes. This can help relieve the pain when you walk.
Questions to Ask

To Prevent Warts
-
•Don’t touch warts on yourself or others.
-
•When you shave a skin area that has a wart, use an electric shaver instead of a razor blade. Or, use an over-the-counter hair remover cream or lotion.
-
•Change shoes often to air them out.
-
•See Self-Care / Prevention for Genital Herpes.
Wear plastic sandals or shower shoes in locker rooms or public pool areas.



Copyright © 2009, American Institute for Preventive Medicine. All rights reserved.