Signs & Symptoms
-
•A strong need to pass urine.
-
•You pass urine more often than usual.
-
•A sharp pain or burning feeling when you pass urine.
-
•Bloody or cloudy urine.
-
•It feels like your bladder is still full after you pass urine.
-
•Pain in the abdomen, back, or sides.
-
•Chills. Fever.
-
•Nausea or vomiting.
-
•A change in mental status, especially if you are over age 70.
Sometimes there are no symptoms with a UTI.
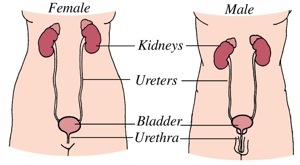
Causes
UTIs result when bacteria infect any part of the urinary tract. The bladder is the most common site.
Persons at Greater Risk for UTIs
-
•Sexually active females.
-
•Females who use a diaphragm for birth control.
-
•Males and females who have had UTIs in the past.
-
•Anyone with a condition that doesn’t allow urine to pass freely. An enlarged prostate gland (in males) and kidney stones are examples.
Treatment
An antibiotic is prescribed to treat the specific infection. Pain relievers are taken as needed. If you get UTIs often, your doctor may order medical tests to find out the problem.