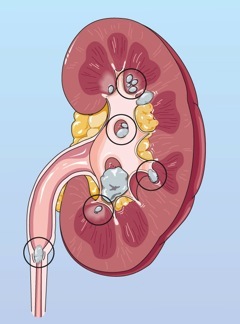
Kidney Stones
Kidney stones are hard masses of mineral deposits formed in the kidney(s). They can be as small as a
tiny pebble or an inch or more across. They are more common in men.
Signs & Symptoms
Some kidney stones cause no symptoms. Small ones can be passed, without pain, when you urinate. When symptoms occur, they include:
-
•Crampy pain that comes and goes. The pain starts in the lower back, travels down the side of the abdomen, and into the groin area. The pain can be severe.
-
•Problems passing urine. You may need to pass urine often. You may pass only small amounts of urine. You may only be able to pass urine in certain positions.
-
•Bloody, cloudy, or dark-colored urine.
-
•Nausea and vomiting. Fever and chills.