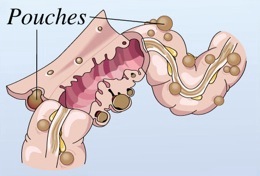
Signs & Symptoms
For Diverticulosis
Often this has no symptoms. Some persons may have:
-
•Mild cramps.
-
•Bloating.
-
•Constipation.
-
•Blood in the stool.
For Diverticulitis
-
•Severe cramping and bloating in the abdomen, usually on the lower left side. The pain is made worse with a bowel movement.
-
•Tenderness over the abdomen.
-
•Nausea.
-
•Fever.
Causes
A low fiber diet is thought to be the main cause. Constipation and overuse of laxatives may also play a role.
Treatment
Diverticulitis needs medical treatment. Diverticulosis can’t be cured, but self-care measures can reduce symptoms and prevent serious problems.